Assuming
that you have understood the array concepts from the above
pre-requisite posts, I would like to explain how to use 'length'
attribute to calculate the number of 2 dimensional arrays, rows and
number of columns in a 3 dimensional array.
Example of a 2 dimensional array -
int a[][][] = new int[2][3][4];
Visual representation of the array -
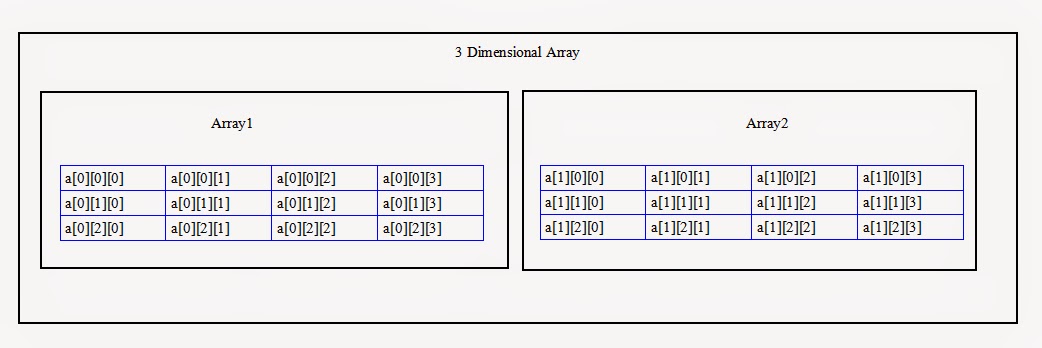
To calculate the number of 2 dimensional arrays in this 3 dimensional array use -> a.length
To calculate the number of rows in the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0].length
To calculate the number of columns in the first row of the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0][0].length
To calculate the number of columns in the second row of the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0][1].length
To calculate the number of columns in the third row of the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0][2].length
To calculate the number of rows in the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1].length
To calculate the number of columns in the first row of the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1][0].length
To calculate the number of columns in the second row of the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1][1].length
To calculate the number of columns in the third row of the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1][2].length
Lets implement this on Eclipse IDE -
1. Launch Eclipse IDE, open Java Project 'Project 018' and create a new Java Class 'Class2' with main( ) method as shown below -
2. Write the following code to print arrays, rows and columns as shown below -

3. Run the java class 'Class2' and observe that the calculation got printed in the console as shown below -
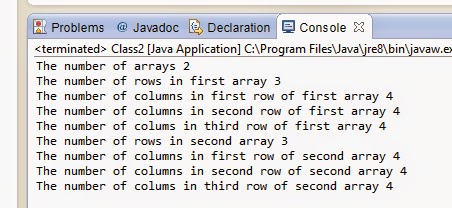
This is how, we use the length attribute in a two dimensional array.
How to work with 'char' data type arrays will be explained in the next post.
Example of a 2 dimensional array -
int a[][][] = new int[2][3][4];
Visual representation of the array -

To calculate the number of 2 dimensional arrays in this 3 dimensional array use -> a.length
To calculate the number of rows in the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0].length
To calculate the number of columns in the first row of the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0][0].length
To calculate the number of columns in the second row of the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0][1].length
To calculate the number of columns in the third row of the first 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[0][2].length
To calculate the number of rows in the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1].length
To calculate the number of columns in the first row of the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1][0].length
To calculate the number of columns in the second row of the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1][1].length
To calculate the number of columns in the third row of the second 2 dimensional array of the 3 dimensional array use -> a[1][2].length
Lets implement this on Eclipse IDE -
1. Launch Eclipse IDE, open Java Project 'Project 018' and create a new Java Class 'Class2' with main( ) method as shown below -

2. Write the following code to print arrays, rows and columns as shown below -

3. Run the java class 'Class2' and observe that the calculation got printed in the console as shown below -

This is how, we use the length attribute in a two dimensional array.
How to work with 'char' data type arrays will be explained in the next post.